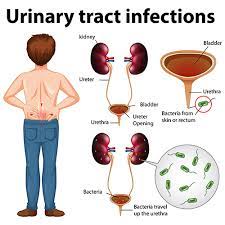
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common bacterial infection that can affect any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, and urethra. While they are more common in women, men can also develop UTIs. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment of UTIs.
Causes of UTIs
UTIs are caused by bacteria, most commonly E. coli, which normally live in the colon. When these bacteria travel from the colon into the urethra and bladder, they can cause an infection. Some factors that can increase the risk of developing a UTI include:
- Being female: Women have a shorter urethra than men, which allows bacteria to travel to the bladder more easily.
- Sexual activity: Sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Menopause: Changes in the urinary tract during menopause can increase the risk of UTIs.
- Medical conditions: Conditions that affect the urinary tract, such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate, can increase the risk of UTIs.
Symptoms of UTIs
The symptoms of a UTI can vary depending on which part of the urinary system is affected. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Frequent urination
- Urgency to urinate
- Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine
- Fatigue or weakness
- Fever or chills
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have a UTI, as untreated infections can lead to more serious health problems.
Treatment of UTIs
UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. Your doctor may also recommend over-the-counter pain relief medication to manage symptoms such as pain or fever. It is important to complete the entire course of antibiotics prescribed by your doctor, even if you start feeling better before you finish the medication.
In addition to antibiotics, there are several strategies you can use to manage the symptoms of UTIs and prevent future infections. These include:
- Drinking plenty of water to help flush bacteria out of the urinary tract
- Avoiding irritants such as caffeine and alcohol
- Wiping from front to back after using the toilet
- Urinating after sexual activity to help flush bacteria out of the urinary tract
- Using a lubricant during sexual activity to reduce irritation and help prevent UTIs
- Taking probiotics, which can help support healthy bacteria in the gut and urinary tract
In some cases, recurrent UTIs may require additional medical intervention, such as long-term antibiotic treatment or surgery to correct an underlying medical condition.
Prevention of UTIs
There are several strategies you can use to help prevent UTIs from occurring. These include:
- Drinking plenty of water to help flush bacteria out of the urinary tract
- Wiping from front to back after using the toilet
- Urinating after sexual activity to help flush bacteria out of the urinary tract
- Using a lubricant during sexual activity to reduce irritation and help prevent UTIs
- Taking cranberry supplements, which may help prevent UTIs by reducing the adhesion of bacteria to the urinary tract
Conclusion
UTIs are a common bacterial infection that can affect any part of the urinary system. Symptoms may include pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, and cloudy or foul-smelling urine. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, and strategies to prevent future infections include drinking plenty of water, wiping from front to back, urinating after sexual activity, using a lubricant, and taking probiotics or cranberry supplements. By taking proactive steps to manage UTIs, you can reduce your risk of developing a more serious infection or complications.