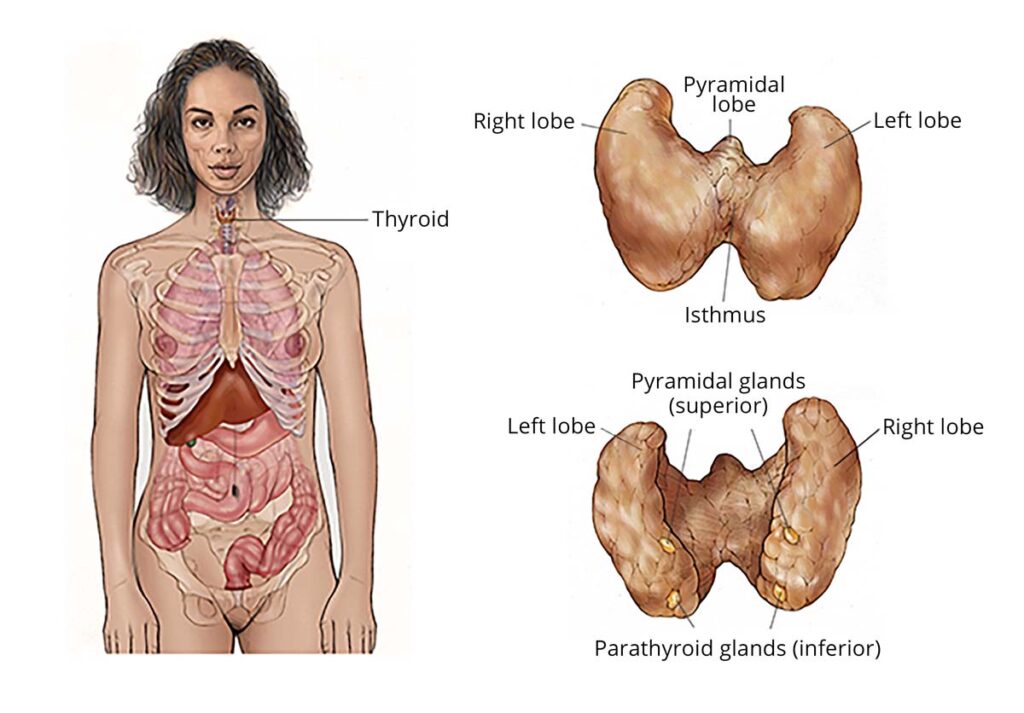
Thyroid cancer occurs in the cells of the thyroid gland and it’s more common among adult
women than men or youth. About 2/ 3rd of cases do in people under age 55. There are
different kinds of thyroid cancer, depending upon the specific cell type within the thyroid
that has come cancerous. Utmost cases of thyroid cancer have good prognostic and
high survival rates, especially when diagnosed in its early stages.
CAUSES OF THYROID CANCER
Thyroid cancer occurs when cells in the thyroid suffer inheritable changes( mutations). The
mutations allow the cells to grow uncontrollably, multiply fleetly and produce a lump. The
cells also lose the capability to announce as normal cells would. The accumulating
abnormal thyroid cells form an excrescence. The abnormal cells can invade the nearby
tissues and can spread throughout the body.
This Exact cause of thyroid cancer isn’t clear but there are a number of effects that can
increase the threat of thyroid cancer include:
- Other thyroid conditions, similar to an inflamed thyroid( thyroiditis) or goiter- but not
a hyperactive - Thyroid or underactive thyroid.
- A family history of thyroid cancer.
- Radiation exposure in childhood( Radiotherapy).
- Obesity
- A bowel condition called familial adenomatous polyposis( FAP).
- Acromegaly, it’s a rare condition where the body produces too much growth
hormone.
THYROID CANCER SYMPTOMS
Thyroid cancer generally doesn’t beget any signs or symptoms beforehand in the disease.
As thyroid cancer grows, it may beget
• A lump, which can be felt through the skin on the neck
• Changes to voice including increasing hoarseness of voice
• Difficulty in swallowing
• Pain in neck and throat
• Swollen lymph bumps in the neck
TYPES OF THYROID CANCER
1. Papillary thyroid cancer: The most common form of thyroid cancer, in papillary
thyroid cancer arises from yearning follicular cells, which produce and store thyroid
hormones. Papillary thyroid cancer can do at any age, but most frequently it affects
people in age 30 to 50.
2. Follicular thyroid cancer( Hurthle cell thyroid cancer): Follicular thyroid cancer also
arises from the follicular cells of the thyroid. It generally affects people aged than
age 50. Hurthle cell cancer of the thyroid gland is a rare and potentially more
aggressive type of follicular thyroid cancer which accounts for only about 3- 10 of all
discerned thyroid cancers.
3. Medullary thyroid cancer: Medullary thyroid cancer usually begins in thyroid cells
called C cells, which produce the hormone calcitonin. Elevated situations of
calcitonin in the blood can indicate medullary thyroid cancer at a veritably early
stage. Certain inheritable runs increase the threat of medullary thyroid cancer,
although this inheritable link is uncommon.
4. Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Anaplastic thyroid cancer is a rare and fleetly growing
cancer that’s veritably delicate to treat. Anaplastic thyroid cancer generally occurs
in grown-ups( age 60 and aged).
5. Thyroid carcinoma(lymphoma): Thyroid carcinoma is a rare form of thyroid cancer
that begins in the vulnerable system cells in the thyroid and grows veritably
snappily. Thyroid carcinoma generally occurs in aged ab grown-ups.
THYROID CANCER TREATMENT
Treatment for thyroid cancer which mainly depends on the type of thyroid cancer and
how far the cancer has spread. The main treatments are
- Surgery: To remove part or all of the thyroid.
- Radioactive iodine treatment: Radioactive iodine( 1- 131), which is an isotope of
iodine can emit radiation. When a small dose of 1- 131 is taken, it’s absorbed
directly into the bloodstream in the gastrointestinal( GI) tract and concentrated
from the blood by the thyroid gland, where it begins destroying the gland’s cells. - External radiotherapy: A machine is used to direct shafts of radiation at the cancer
cells to kill them. - Chemotherapy and targeted curatives: specifics used to kill cancer cells.
What are early warning signs of thyroid cancer?
Thyroid cancer may not cause any noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as cancer grows, it can cause several signs and symptoms, including:
- A lump or swelling in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Neck or throat pain
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
- Persistent cough that is not related to a cold or allergies
- Fatigue or weakness
- Unexplained weight loss
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other medical conditions, and having these symptoms does not necessarily mean that a person has thyroid cancer. However, if you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Is thyroid cancer very curable?
The prognosis for thyroid cancer is generally very good, with a high chance of cure, especially for the most common types of thyroid cancer. The treatment and outcome of thyroid cancer depend on the type and stage of the cancer.
In most cases, thyroid cancer is treated with surgery to remove the thyroid gland and any cancerous tissue. In some cases, radioactive iodine therapy may also be recommended to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
The outlook for thyroid cancer is generally favorable, with a five-year survival rate of around 98% for the most common types of thyroid cancer. However, in rare cases, thyroid cancer may be more aggressive and less responsive to treatment, leading to a lower survival rate.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate treatment plan and to receive regular follow-up care to monitor for any potential recurrence of thyroid cancer.
Is thyroid cancer very serious?
Thyroid cancer is a serious condition that requires prompt and appropriate treatment. However, the severity of thyroid cancer can vary depending on the type and stage of cancer.
In general, the most common types of thyroid cancer have a good prognosis and a high chance of cure. Treatment typically involves surgery to remove the thyroid gland and any cancerous tissue, along with potential radiation therapy or other treatments. With proper treatment, most people with thyroid cancer are able to live long, healthy lives.
However, in rare cases, thyroid cancer may be more aggressive and less responsive to treatment, leading to a lower survival rate. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate treatment plan and to receive regular follow-up care to monitor for any potential recurrence of thyroid cancer.