Syphilis is sexually transmitted infection (STI) which is caused by the spirochete
bacterium called Treponema pallidum. This disease can be transmitted to another person through kissing or close physical contact. The infected individual unwittingly transmits the syphilis illness to his or her sexual partner since they are frequently unaware that they are sick.
STAGES OF SYPHILIS:
The symptoms of syphilis is usually developed in three stages, are discussed below:
• Stage 1( Primary syphilis): Symptoms of syphilis begin with a effortless but largely contagious sore present on the genitals or also occasionally around the mouth. However, especially during sexual contact, they can also come infected with syphilis, If somebody else differently comes into close contact with the sore. The generally sore lasts two to six weeks before fading.
• Stage 2( Secondary syphilis): Secondary symptoms, include skin rash and sore throat may develop. These secondary symptoms may vanish within a many weeks, after which a person may witness a latent( hidden) phase with no symptoms, which can last for times. After this, syphilis can progress to its third stage which is most dangerous stage.
• Stage 3( Tertiary syphilis): Around one third of people who aren’t treated for
syphilis will develop tertiary syphilis. At this stage, it can beget serious damage to
the body.
SYPHILIS SYMPTOMS:
The symptoms of syphilis are the same both men and women. Also symptoms are mild and therefore can be difficult to recognize the symptoms. The symptoms develop in three stages,
Primary syphilis
Secondary syphilis
Tertiary syphilis
Primary Syphilis:
The original symptoms of syphilis can generally appear at time between 10 days to three months after one has been exposed to the infection. The most common symptom is the appearance of a small, effortless sore or ulcer( called chancre).The area of the body where the infection was contracted will develop the sore, which is often the penis, vagina, anus, rectum, tongue, or lips. Utmost people only have one sore, but some people can have further.
The blisters are effortless and may be overlooked, so the condition can be spread without realizing that they have an infection.
The sore will also vanish within two to six weeks and, if the condition is not treated, syphilis will move into its secondary stage.
Secondary Syphilis:
The symptoms of secondary syphilis will generally begin many weeks after the exposure of the sore. Common symptoms include
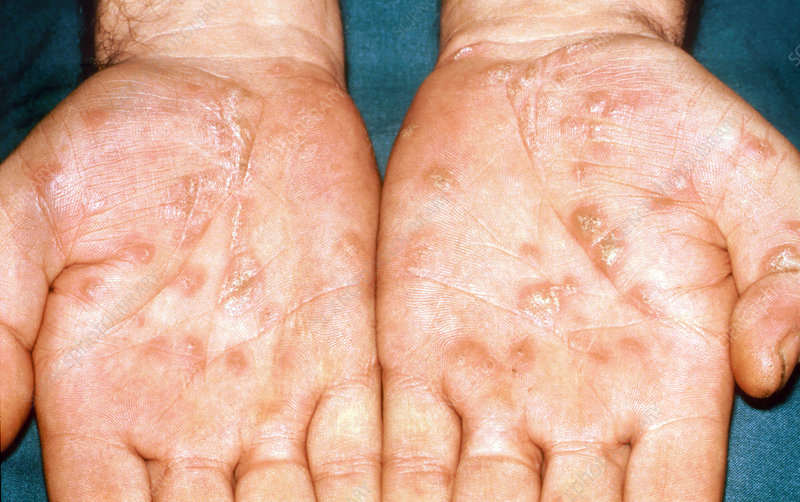
- A non-itchy skin rash appears anywhere on the body, but generally on the triumphs of the hands or soles of the bases,
- Tiredness
- Headaches
- Swollen lymph glands
Less common symptoms include
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Patchy hair loss
- Pains in joints
- The symptoms of this disease will disappear within a short period of weeks or may redevelop for some period of months. Latent Phase:
- Syphilis will undergo dormant phase (latent or hidden),in this phase there are no symptoms even if the person is infected.However,still the latent syphilis can be
transmitted to another person through sexual or close physical contact during the first year of this stage. After a few years, the illness no longer spreads from one person to another, but the individual who already has it will continue to be sick. - The dormancy of this infection in latent stage is un predictable, which may occur for many years or last for even decade.
- Without proper treatment, there is a risk that latent syphilis will then move on to
the most dangerous stage called tertiary syphilis.Tertiary Syphilis:
Further proceeding from latent stage to tertiary stage, the duration for the symptoms of this infection can begin after many years or even for decades. About one third of people with syphilis infection will produce severe symptoms at this tertiary stage. -
SYPHILIS IS CAUSED BY:
Syphilis is caused by the bacteria Treponema palladium.
The bacteria can enter one’s body when he/she has close contact with an infected sore, normally during vaginal, anal or oral sex or by sharing sex toys.DIAGNOSIS OF SYPHILIS:
- Physical examination: Syphilis can be diagnosed by the genital examination. For men,It involves examination of the penis, urethra( the hole at the end of the penis where urine comes out)and foreskin. For women, diagnosis of syphilis involves an internal examination of the vagina. For both men and women may anus is examined.
- Blood tests:If one is infected with syphilis, also his/ her body produces antibodies (proteins released as part of a vulnerable response) against the syphilis bacteria. Thus, A blood sample can be examined for the presence of these antibodies as one technique to detect if someone has syphilis. A positive result( antibodies present) indicates that one can moreover have the infection or used to have it( because the antibodies can remain in the body for times, indeed after a former infection was successfully treated). A negative result doesn’t inescapably mean that bone doesn’t have syphilis as the antibodies may not be sensible for three months after infection. Person may be advised to follow up the test in regular three months’ time. Every pregnant woman should have a blood test for syphilis as the infection can kill future or new born babies. The blood test is generally done during a prenatal appointment at weeks 11- 20 of pregnancy. However, treatment for both the mother and baby can begin, If the test is positive.
- Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test( VDRL): The VDRL test is nothing but a webbing test to diagnose syphilis. This test measures the substance called as antibodies that body may produce if a person comes in contact with the bacteria that causes syphilis. This bacteria is called Treponema pallidum.
- Swab test: If blisters or sores are present, a swab( like a cotton cub) will be used to take a small sample of fluid from the sore. This is also either looked at under a microscope in the clinic or transferred to a laboratory for examination.
SYPHILIS TREATMENT:
Effective antibiotic treatment is available. Treatment needs to be supervised precisely and long- term follow- up is needed, particularly for cases with late stage syphilis infection. Treatment of the mother during gestation may be sufficient to help fetal infection. Occasionally babies bear an fresh course of antibiotics after birth. Primary Option: Penicillin G Benzathine2.4 million units intramuscularly as a single cure. Secondary Option: Doxycycline 100 mg Orally doubly diurnal and Prednisone 40- 60 mg orally formerly daily for 3 days; start 24 hours before penicillin.
PREVENTION:
- Defended physical contact through the use of condoms reduces the threat of infection.
- Promoting sex- education among teenagers.
- Furnishing mindfulness among the population about their sexual health. To
especially in high pitfalls population( high pitfalls population involves coitus workers and their mates, Intravenous medicine druggies, truck motorists, labour settlers, deportees and captures). - People with syphilis should refrain from any sexual contact for at least 1 week after completing treatment or until the lesions of early syphilis( if they were present) are completely healed.
- People with syphilis should also refrain from any sexual contact until sexual
partners have been communicated , tested and if indicated treated. - Blood tests must be done on regular basis to make sure that treatment has cleared the infection.
- Pregnant women are screened for syphilis in early gestation and again in late
gestation if they’re at increased threat of acquiring syphilis - Testing to count other sexually transmitted infections is judicious.
SYPHILIS TREATMENT:
Effective antibiotic treatment is available. Treatment needs to be supervised precisely and long- term follow- up is needed, particularly for cases with late stage syphilis infection. Treatment of the mother during gestation may be sufficient to help fetal infection. Occasionally babies bear an fresh course of antibiotics after birth. Primary Option: Penicillin G Benzathine2.4 million units intramuscularly as a single cure. Secondary Option: Doxycycline 100 mg Orally doubly diurnal and Prednisone 40- 60 mg orally formerly daily for 3 days; start 24 hours before penicillin.
PREVENTION:
• Defended physical contact through the use of condoms reduces the threat of
infection.
• Promoting sex- education among teenagers.
• Furnishing mindfulness among the population about their sexual health. To
especially in high pitfalls population( high pitfalls population involves coitus workers and their mates, Intravenous medicine druggies, truck motorists, labour settlers, deportees and captures).
• People with syphilis should refrain from any sexual contact for at least 1 week after finishing the prescribed course of therapy or until the early syphilis lesions, if any, have fully disappeared.
• People with syphilis should also refrain from any sexual contact until sexual
partners have been communicated, tested, and if indicated treated.
• Blood tests must be done on regular basis to make sure that treatment has cleared the infection.
• Pregnant women are screened for syphilis in early gestation and again in late
gestation if they’re at increased threat of acquiring syphilis
• Testing to count other sexually transmitted infections is judicious.

Wow, awesome blog layout! How long have you been blogging for?
you make blogging look easy. The total glance of your site is magnificent, let
alone the content! You can see similar: sklep online and here
sklep online
thank you