Scarlet fever is also known as Scarlatia. It is a bacterial infection with pyrogenic
exotoxin(erythrogenic toxin) producing group A streptococcus(GAS) in individuals who do not have antitoxin antibodies. It is a URT(upper respiratory tract) infection associated with a characteristic red rash and sore throat. Scarlet fever rash may reflect a hypersensitivity throat reaction requiring prior exposure to the toxin. It occurs mostly in children aged 4-8 years.
SCARLET FEVER SYMPTOMS:
• Fever 38 C Or high
• Chills Abdominal pain
• Headache
• Dysphagia
• Tachycardia
• Seizures
• Exanthem
• Swollen glands in the neck
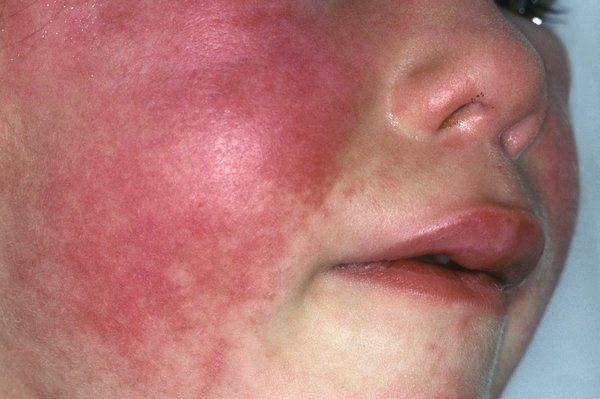
• Red rash Cause Flush face with pale area around the face
• Red colour throat and sore throat
• Red lines
• Body aches
• Strawberry (red and bumpy) tongue
• Difficulty in swallowing
• Skin pigmentation
• Nausea and vomiting
• Whiting coating on the tongue early in the illness
Rashes and redness on face and tongue usually last for a week
Click Here To Buy
SCARLET FEVER RASH:
• It begins on the first days after the illness. It is a red colour rash that usually
appears.
• The rash may first be developed on the neck, underarm and groin.
• The rash spread all over the body
• The rash usually begins as small, flat blotches slowly become fine bumps.
EXANTHEM:
• Exanthem is nothing but a diffuse rash. It is caused by many viruses including
chicken pox, rubella, adenovirus, enterovirus etc.
• It causes red or pink colour spots on the skin over large parts of the body.
• It is a widespread rash that usually occurs in children.
MODE OF TRANSMISSION:
• GAS infection causes scarlet fever are contagious.
• It can spread from one person to another by breathing in airborne droplets from an Infected person’s coughing or sneezing.
• It can spread by sharing personal belongings such as cloths , bed linen, towels etc
• Also spread by infected individuals who are carriers of streptococcal bacteria but do not show any symptoms
• It usually takes around 5 days for someone exposed to group A streptococcus
bacteria sick with strep throat or scarlet fever
What is the incubation period of scarlet fever?
The incubation period of scarlet fever is around 3-6 days
SCARLET FEVER IS CAUSED BY?
• Scarlet fever is caused by streptococcus pyrogens, certain strains of group A
streptococcus. In scarlet fever streptococcus bacteria release a pyrogenic exotoxin, which produces the rash and red tongue
• The pyrogenic exotoxin are of three types i. e A ,B and C. All three are capable of producing scarlet fever
RISK FACTORS OF SCARLET FEVER:
• People living in overcrowded environment
• Children older than 3 years
• People in close contact with someone who has a strep throat or skin infections
COMPLICATIONS OF SCARLET FEVER:
• Rheumatic fever: disease which affects the heart, joints, brain and skin
• Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis: inflammation of the kidney, which presents 1-2 weeks after a group A strep pharyngitis
• Arthritis:joint inflammation
• Neurologic complications
• Pneumonia :lung infection
• Otitis media
• Septicaemia
• Osteomyelitis
• Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome
• Meningitis
• Peritonsillar abscess
• Toxic myocarditis
• Ear infection
• Kidney damage
• Hepatitis
PREVENTION OF SCARLET FEVER:
• Wash your hand regularly
• Avoid sharing your belongings like eating utensils, linens, towels etc
• Children with scarlet fever should stay home at least 24 hours after starting
antibiotics
• Take bed rest
• Cover your mouth and nose
• Don’t touch your face after sneezing or coughing
• Use hand sanitizer
HOME REMEDIES FOR SCARLET FEVER:
• Take otc medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, which helps to control the pain and reduces the fever
• Take plenty of water or other fluids
• Use throat lozenges which provide temporary relief from the sore throat
• Gargling with warm salt water also give relief from the sore throat
DIAGNOSIS OF SCARLET FEVER:
Clinical diagnosis supported by lab investigators
• Rapid streptococcal test: this test involves swabbing of the throat and conducting a test using swab. The test detects the presence of group A streptococcus.
• Physical examination : checking inflammation of tonsils, pharynx and larynx Throat culture: Culturing of the swab. Helps to detect the group A streptococcus bacteria. But this test takes too much time for culturing.
• Serologic: positive for antistreptolysin o titers and Anti-deoxyribonuclease B
• Complete blood count(CBC):A complete blood count test is also called a full blood count. The test includes an actual counting of wbc and rbc cells. CBC test is a routine test done to monitor the overall health condition of the body.
The components of the CBC are
1. RBC(red blood cells)
Normal range – For male:4.7-6.1million cells/mcL
For female:4.2-5.4 million cells/mcL
2. WBC(white blood cells)
Normal range is 4500-11000 cells/mcL
3. Platelets
Normal range is 150000-450000 cells/mcL
• Differential diagnosis :It may be distinguished by pattern of symptoms
Viral Exanthem
Dry eruption
Kawasaki disease
Toxic shock syndrome
Contact dermatitis
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Measles
Early stage of smallpox
TREATMENT OF SCARLET FEVER:
There is no specific vaccine to prevent or to treat strep throat or scarlet fever.
Medication: the drug of choice for scarlet fever is Antibiotics
Antibiotics help to kill the bacteria that are responsible for throat infection . Examples of antibiotics include penicillin, erythromycin etc.
Use of antibiotics in scarlet fever include
• Decreasing symptoms
• Preventing the bacterial infections
• Preventing complications like rheumatic fever