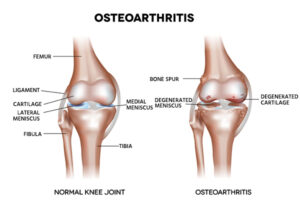
OSTEOARTHRITIS:
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis which affects millions of people around the world. Osteoarthritis is an degenerative disorder,which is arising from the biochemical catabolism of hyaline(articular)cartilage which is present in the synovial joints. However, the current view states that osteoarthritis not only involves the articular cartilage but also include the entire joint organ, including hands, neck, knees ,lower back and hips.
Nearly about 250 million people are suffering from osteoarthritis of the knee (approximately 3.6%of the population). In the United States approximately about 27 million people are affected by osteoarthritis. It is estimated that about 80% of the world population have radiographic evidence of osteoarthritis by age of 65 years,although only 60% of those will have symptoms.This disorder will cause moderate to severe disability in 43.4 million people.
TYPES OF OSTEOARTHRITIS:
There are mainly two types of osteoarthritis includes,
1. Primary osteoarthritis:
This type of osteoarthritis is related to aging. With aging, the water content of the
cartilage gradually increases, and the protein makeup of cartilage degenerates.
2. Secondary osteoarthritis:
This type of osteoarthritis is caused by another disease or condition. Conditions that can cause secondary osteoarthritis include obesity, repeated trauma or surgery to the joint structures, abnormal joints at birth (congenital abnormalities), gout, diabetes, and other hormone disorders.
WHAT CAUSES OSTEOARTHRITIS:
Osteoarthritis will occurs when the cartilage that cushions the each ends of bones in the joints gets deteriorates over the time. Cartilage is a firm, frictionless joint motion. The surface of the hyaline cartilage will becomes very rough in case of osteoarthritis. Slippery tissue that permits nearly The daily stresses which is applied to the joints, particularly the weight-bearing joints such as knee, ankles and also hip, plays an important role in the development of osteoarthritis.
Most investigators will believe that degenerative or alterations in osteoarthritis primarily begin in the articular cartilage, as a result of either excessive loading of a healthy joint or relatively normal loading of a previously disturbed joint. External forces will increase or accelerate the catabolic(breakdown)effects of the chondrocytes and further disrupt the cartilaginous matrix.
Knee osteoarthritis is categorised as either primary osteoarthritis ( also called idiopathic) or secondary osteoarthritis. There are various structures helps in making up the knee joint in that the hyaline cartilage joint is the main target of the harmful influences which cause osteoarthritis and the structure in which their osteoarthritis disease begins. Approximately about 95% of the hyaline cartilage will consists of extracellular matrix.
• Older age: The risk of osteoarthritis increases with age.
• Sex: Women are more prone to develop osteoarthritis than men, though the reason behind is unknown.
• Obesity(overweight): Carrying more body weight will stresses to the joints,
particularly the weight- puts added stress on weight-bearing joints, such as knees,
ankle and hips.
• Joint injuries: joint Injuries including those that occur when playing sports or due to accident, may also increase the risk of causing Osteoarthritis
• Genetics (significant family history)
• Reduced levels of sex hormones Muscle weakness
• Repetitive use (jobs requiring heavy labour and bending) Infection
• Crystal deposition in joints
• Acromegaly
• Previous inflammatory arthritis(e.g. burnt-out rheumatoid arthritis)
• Heritable metabolic which causes (e.g., alkaptonuria, hemochromatosis, and Wilson disease)
• Hemoglobinopathies (e.g., sickle cell disease and thalassemia) Neuropathic
disorders which leads to a Charcot joint (e.g., syringomyelia, tabesdorsalis and also diabetes)
• Underlying morphologic risk factors include (e.g., congenital hip dislocation and
slipped femoral capital epiphysis) bone disorders (e.g., Paget disease and avascular necrosis)
• Previous surgical procedures(e.g.,meniscectomy)
OSTEOARTHRITIS SYMPTOMS:
Osteoarthritis symptoms will develop slowly and worsen over time. Signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis include:
• Severe Pain: Joint may hurt during or after movement. Tenderness: Joint may feel tender even if the light pressure is applied on joints.
• Stiffness: Joint stiffness may be most noticeable when waking up in the morning or after a prolonged period of inactivity.
• Loss of flexibility: feel difficulty in movement of joints through its full range of
motion.
• Grating sensation: May hear or feel a grating sensation when moves the joint.
• Bone spurs: These extra bits of bone, which feel likes a hard lumps, will form
around the affected joint.
DIAGNOSIS OF OSTEOARTHRITIS:
The osteoarthritis can be diagnosed by using following tests
• Physical exam: conduct physical examination of the affected joint includes,
checking for tenderness, swelling or redness of the joints.
• Imaging tests: taking pictures of the affected joints can be obtained during imaging tests. Examples include:
• X-rays: An X-ray may helps to detect the bone spurs around a joint. Many people have X-ray evidence of osteoarthritis before they experience any signs and symptoms.
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI can be helpful in determining what exactly is causing pain.
• Lab tests: this test is done by analysing blood or joint fluid can help to pinpoint the diagnosis.
• Blood tests: Blood tests may help to rule out other causes of joint pain, such as
rheumatoid arthritis.
• Joint fluid analysis: By taking fluid from the affected joint for inflammation and pain is caused by gout or an infection
TREATMENT FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS:
There is no known cure for osteoarthritis, but treatments can help to reduce pain and are able to maintain movement of joints. Medications: Osteoarthritis symptoms can be relieved by using a variety of medications, including:

ARTHOREX Joint Pain Relief Tablets | Joint Support Supplement for Men & Women | Ayurvedic Tablets for Arthritis & Cervical Pain | Boy Now
• Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen can helps to relieve joint pain, but it does not
reduce inflammation of joint.
• NSAIDS:NSAIDS may reduce joint inflammation and relieve pain. NSAIDs
medications include Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Diclofenac sodium, Aceclofenac and Naproxen.
• Narcotics: Narcotics like codeine and may provide relief from more severe
osteoarthritis pain. Lifestyle and home remedies: changes in lifestyle and home
treatments also can help to reduce osteoarthritis signs and symptoms.
• Rest: Experiencing pain or inflammation in joint the take rest for atleast 12 to 24
hours.
• Exercise: Proper exercise can increase endurance and strengthen the muscles
present around joint and making joint more stable.
• Lose weight: Being overweight or obese increases the stress on weight-bearing
joints, such as ankles,knees and even in hips. Even a small amount of weight loss
can relieve some pressure on joints and reduce pain.
• Use heat and cold to manage pain: Both heat and cold can helps to relieve pain in joints. Heat also relieves stiffness, and cold can relieve muscle spasms and pain.