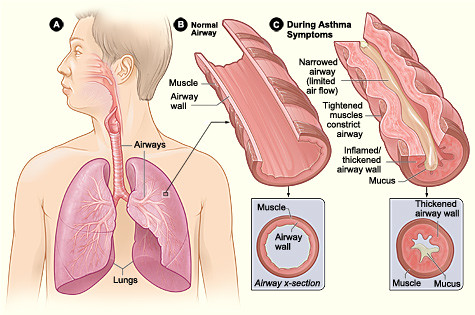
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airway that is associated with airway hyperresponsiveness and inflamed, blocked, and narrowed airways. Asthma is characterized by recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and cough particularly at night /in the morning. Asthma can occur in any age group of people. Asthma is a type -1 hypersensitivity reaction. In a non-asthmatic person(normal person), the muscles around the bronchial tubes are relaxed, consisting of the normal amount of mucus, and the tissue is thin thus allowing for easy airflow.
ASTHMA SYMPTOMS:
The main symptoms of asthma include,
- Dyspnoea (shortness of breath)
- Wheezing (whistle sound during respiration)
- Cough (particularly at night)
- Chest tightness
- Sleep problems
- Feeling tired
- Allergies
- Common cold
Omron Wheeze Scan – Portable Wheeze Detector for Analysis of Children’s Breathing Noise – Helps with Asthma Symptoms
TYPES OF ASTHMA:
There are mainly three types of asthma includes,
1. Atopic asthma/Allergic asthma/Extrinsic asthma:
This is a common type of asthma. About 70% of patients suffer from atopic asthma. It begins in childhood or in early adulthood. Genes inherited from parents make the immune system overreacts to harmless stimuli and produces too much IgE antibody.
2. Non-atopic asthma/Non -allergic asthma/Intrinsic asthma:
This type of asthma is less common. Not related to an allergy trigger. It usually develops in adult life with negative personnel/ family history and normal serum level of IgE.
3. Mixed asthma:
This is the combination of both allergic and nonallergic asthma. This
is the most common form of asthma.
Other types of asthma include,
• Cough variant asthma:
This type of asthma does not have the symptoms of asthma such as wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Instead, it is characterized by only one symptom i,e a persistent dry cough.
• Exercise-induced asthma:
This type of asthma affects the person during or after physical activity.
• Occupational asthma:
This type of asthma is induced by triggers that exist in a person’s workplace including textiles, farming, and woodworking.
• Eosinophilic asthma:
Due to high levels of WBC(Eosinophils). Usually occurs between 35-50 years old.
• Aspirin-induced asthma:
Aspirin, along with a runny nose, sneezing, sinus pressure, and cough can asthma symptoms.
What are the causes/trigger factors of asthma?
Triggers are the combination of environmental and genetic factors,
1. Airborne allergens
2. Respiratory tract infections
3. Physical activity
4. Cold air
5. Air pollution
6. Medication
7. Food allergy
8. Strong emotions/stress
9. Irritants
10. Family history
11. Pet danger
What are clinical manifestations?
• Wheezing, dyspnoea, and cough
• Variable – both spontaneously and with therapy
• Tenacious mucus production.
• Symptoms worse at night
• Non-productive cough
• Limitation of activity
PREVENTION OF ASTHMA:
• Reducing exposure to allergens
• Take preventive medication
• Avoid smoke of any type
• Avoid triggers
• Everyday cleaning
• Boosting immunity by eating foods rich in antioxidants
• Avoid extreme cold
DIAGNOSIS OF ASTHMA:
Asthma can be diagnosed by using the following tests,
1. Physical exam:
The physician will look for the signs and symptoms of asthma and its related conditions. They will look at the person’s eyes, nose, and skin and listen to the chest and lungs. In a physical exam, they use a device called a pulse oximeter which measures the levels of oxygen in the body.
2. Pulmonary function test:
This test is also called as lung function test. This test is performed to check the breathing (inhale and exhale) in patients. These tests include,
• Spirometry: It is a type of pulmonary function test, which measures how much
you breathe in and out and the rate of breathing.
• FeNO test(nitric oxide test): This test helps to detect inflammation in
the airways.
• Allergy test: allergy is one of the symptoms of asthma.
3. Blood test:
This test will provide information regarding the amount of WBC cells (eosinophils) and IgE antibodies. If the level is high, then it may be a sign of asthma.
TREATMENTS FOR ASTHMA:
Medications which is prescribed for the treatment of asthma will reduce the
asthma symptoms
1. Bronchodilators:
This type of medication will relax the smooth muscle around the airways and is used for chronic asthma. Mainly there are three types of drugs in bronchodilators,
• Beta 2 sympathomimetics:
Gives action like a beta 2 receptor agonist. Decrease
the inflammation. These are the most effective and fastest-acting bronchodilators
through inhalation.
SABA: short-acting Beta 2 agonist and fast onset of action
LABA: long-acting Beta 2 agonist and slow onset of action
• Methylxanthines:
These give their action decrease bronchoconstriction.
• Anticholinergics:
These will prevent the tightening of smooth muscles around the airways
2. Anti-inflammatory medicines:
These will reduce the swelling and mucus production in the airways and makes them breathe easier.
3. Leukotriene receptor antagonist:
these will reduce bronchoconstriction, mucus production, and inflammation
4. Mast cell stabilizers:
These will decrease inflammation by preventing the degranulation of mast cells, which is responsible for the release of inflammatory mediators.
5. Anti-IgE antibodies:
They neutralize free IgE Antibodies getting produced during asthma.
6. Corticosteroids:
These are not bronchodilators, they give their action by producing anti-inflammatory action. There are two types of corticosteroids
• Inhaled corticosteroids
• Systemic corticosteroid
what you need to know about asthma
EuroMedica CuraPro – 750 MG, 120 Softgels – High Potency Turmeric Curcumin Supplement – Clinically-Studied Liver, Brain, Heart & Immune Support – 120 Servings. Buy Now

Click Here To Buy