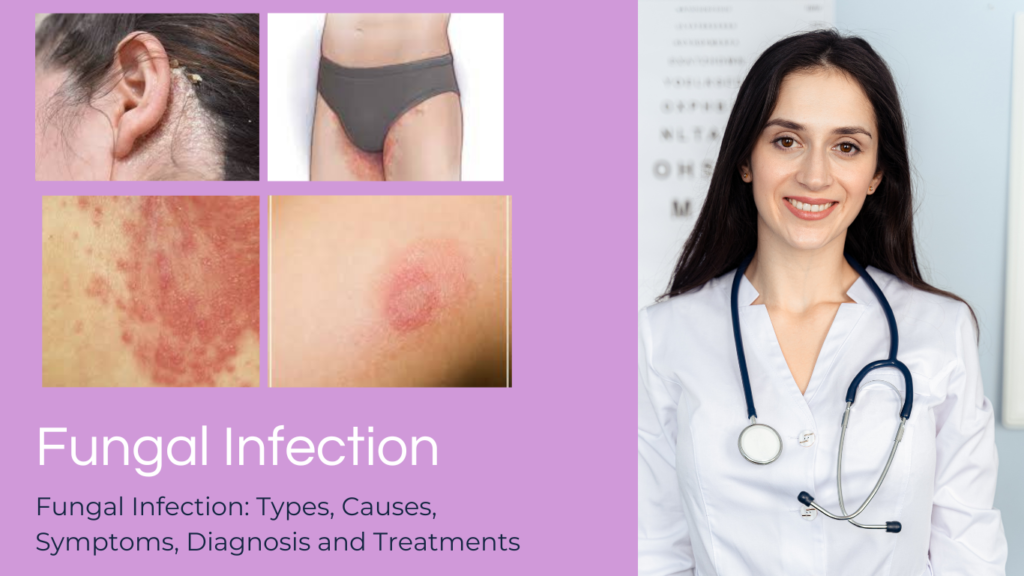
The infections caused by various types of fungus (Mold or yeast) are called fungal infections. Fungi are eukaryotes that grow by the process of budding or by filamentous extension. This invades the tissue confined to the skin, even spreads into bones, tissue, and organs, or may affect the whole body. There are over 100,000 fungal species in that 150 species are pathogenic in nature. Fungi are mainly present in the environment and even can enter the individual through inhalation, ingestion, or direct contact. Most of the infections are mild and self-limited but can be severe if not treated. The development of fungal infection depends on the dose, site of infection, virulence, and immunological status of the host.
FUNGUS
Fungus is a colorless plant lacking chlorophyll. yeasts, Molds, rusts, and mushrooms will fall under the fungal kingdom. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophic means they obtain nutrients from the environment but not from endogenous sources (like plants with photosynthesis). Most of the fungi are beneficial and are involved in bio-degradation
reactions, however, a few can cause opportunistic (affecting patients only or chiefly when the immune system is depressed) infections, if they are introduced into the skin through wounds or into the lungs and nasal passages if inhaled. Fungi that cause disease in humans may be like yeast or hyphae (mold) and are called mycotic infections.
TYPES OF FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Fungal infections may be any one of the following types namely,
1) Superficial mycotic infections are those that occur on the skin’s surface or just beneath the skin or nail and are caused by dermatophytes from the genera Microsporum, Trichophyton, or Epidermophyton. These dermatophytic infections are called from the place of infection rather than the organism that causes them.
i) Athlete’s foot (Tinea pedis): This type of fungal infection affects the skin of the feet particularly in between the toes. It may cause redness, skin peeling, itching and sometimes it may cause blisters.
ii) Ringworm (Tinea corporis): This type of fungal infection is caused by a fungus, not by ringworm. It affects the surface of the skin on various body parts characterized by circular, red, and scaly patches. It is highly contagious and this may be transmitted through direct contact with infected animals or infected persons.
iii) Jock itch (Tinea crusia): This fungal infection affects the inner thighs, buttocks, in the groin area. It is most common in males when compared to females. It causes symptoms like redness. Itching, rash, and a person may feel a burning sensation.
2) Cutaneous fungal infections
i) Nail fungus (Onychomycosis): Fungal infections can also affect the nails, usually on the toes. Infected nails with fungus may become thickened, discolored, brittle, and may even separate from the nail bed.
ii) Oral thrush (Oral candidiasis): This fungal infection is caused by the Candida fungus and affects the mouth and throat. It can cause white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and roof of the mouth, along with discomfort and difficulty swallowing.
iii) Vaginal yeast infection (Vulvovaginal candidiasis): This common fungal infection affects the vaginal area in women. It can cause itching, burning, abnormal discharge, and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
3) Systemic mycotic infections occur throughout the body, such as the lungs and other organs. Because of favorable temperatures for their reproduction, many of the species that cause systemic fungal infections are restricted to certain geographic areas.
i) Aspergillosis: It is a fungus infection caused by mold i.e. Aspergillus. People with weakened immune systems and lung infections are more susceptible to developing this type of infection.
ii) Cryptococcosis: It is a fungal infection caused by cryptococcosis neoformans. It affects mainly the lungs and brain. It is a very rare type of infection.
iii) Histoplasmosis: It is a common fungal lung infection caused by Histoplasma
CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS
Fungal infections are caused by various types of fungal pathogens and Factors that increase susceptibility to fungal infections
1. Weakened immune system
2. Prolonged antibiotic use
3. Diabetes
4. Poor hygiene
5. Environmental factors
FUNGAL INFECTION SYMPTOMS
Symptoms of a fungal infection can vary depending on the type and location of the infection, but common symptoms may include:
• Itching, redness, or swelling on the skin
• Scaling or peeling of the skin
• Pain or discomfort in the affected area
• Thickening or discoloration of the nails
• Difficulty breathing or coughing (in cases of lung infections)
• In situations of oral thrush, white spots or ulcers in the mouth or throat
Depending on the nature and severity of the illness, fungal infections can be treated with a number of antifungal drugs that can be administered locally or taken orally. Aside from medicine, personal cleanliness and avoiding situations where fungi flourish can help to prevent fungal infections. If you believe you have a fungal infection, get medical assistance immediately to ensure an accurate diagnosis and suitable treatment.
DIAGNOSIS OF FUNGAL INFECTION
1. Physical examination: A healthcare professional will examine the affected area, looking for characteristic signs such as redness, itching, scaling, or other skin changes. They may also assess the nails, hair, or mucous membranes for any visible fungal infection symptoms.
2. Microscopic examination: In some cases, a sample of the affected tissue, skin scrapings, nail clippings, or discharge may be collected and examined under a microscope. This can help identify the presence of fungi or their characteristic structures.
3. Culture tests: A sample of the affected area may be collected and cultured in a laboratory to grow and identify the specific type of fungus causing the infection. This can help determine the most effective antifungal treatment.
4. Molecular tests: In certain cases, molecular tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) may be used to detect and identify specific fungal DNA or genetic material. These tests are particularly useful for identifying difficult-to-culture or uncommon fungal species.
FUNGAL INFECTION TREATMENT/
BEST ANTIFUNGAL CREAM FOR PRIVATE AREA /BEST ANTIFUNGAL CREAM/ANTIFUNGAL OINTMENT
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for the appropriate antifungal cream to use for a fungal infection in the private area. The type of antifungal cream recommended may vary depending on the specific type of fungal infection, as well as the severity of the infection and the patient’s medical history.
Some commonly recommended antifungal creams for fungal infections in the private area include:
1. Clotrimazole cream: commonly used to treat yeast infections, jock itch, and ringworm in the groin area.
2. Miconazole cream: used to treat fungal infections of the skin, including those in the groin area.
3. Terbinafine cream: used to treat fungal infections of the skin, including jock itch and ringworm.
When using an antifungal cream, it is critical to follow the guidelines supplied by a healthcare practitioner and to continue using the cream for the complete course of therapy, even if the symptoms improve. Seek medical treatment if your symptoms do not improve or worsen after taking an antifungal cream.
ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS /ANTIFUNGAL TABLET
Antifungal drugs are medications used to treat fungal infections caused by fungi that can infect the skin, nails, hair, and internal organs. There are several classes of antifungal drugs, including.
Azoles: these are broad-spectrum antifungal drugs that work by inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a key component of fungal cell membranes. Examples of azoles include fluconazole,, voriconazole, itraconazole and
posaconazole
Polyenes: these antifungal drugs work by binding to fungal cell membranes and causing them to leak, leading to the death of the fungus. Examples of polyenes include amphotericin B and nystatin.
Allylamines: these drugs work by inhibiting the production of ergosterol, leading to the death of the fungus. Examples of allylamines include terbinafine and naftifine.
Echinocandins: these drugs work by inhibiting the production of beta-glucan, a key component of the fungal cell wall, leading to the death of the fungus. Examples of echinocandins include micafungin, caspofungin, and anidulafungin.
Griseofulvin: this antifungal drug works by binding to the microtubules in fungal cells, inhibiting their growth and replication.
Antifungal drugs can be administered orally, topically, or intravenously, depending on the type and severity of the fungal infection. The choice of antifungal drug and mode of administration is typically determined by a healthcare professional. It is important to take antifungal drugs exactly as prescribed and to complete the full course of treatment,
even if the symptoms improve. Common side effects of antifungal drugs include gastrointestinal upset, liver toxicity, and allergic reactions.
ANTIFUNGAL POWDER
Antifungal powder is a type of powder that is formulated with antifungal agents to help prevent or treat fungal infections on the skin. These powders are typically used for conditions such as athlete’s foot, jock itch, and ringworm. The active ingredients in antifungal powders can vary depending on the brand, but common ingredients include:
1. Clotrimazole: This is an antifungal medication that can be used in powder form to help treat fungal infections.
2. Miconazole: this is another antifungal medication that can be used in powder form to treat fungal infections.
3. Tolnaftate: This is an antifungal medication that is often used in combination with other ingredients in antifungal powders.
Antifungal powders are typically applied to the affected area of the skin after showering or bathing. The powder should be gently rubbed into the skin to ensure that it is fully absorbed. It is important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer of the antifungal powder and to use the powder regularly as directed to help prevent the recurrence of fungal infections.
Buy. https://amzn.to/3uDH0iG
https://amzn.to/3N2AGb8