Acquired Hemolytic anemia is a condition in which there’s the destruction of RBC cr junking of red
blood cells from the rotation before their normal life span of 120 days. Numerous
conditions, conditions, and factors can beget the body to destroy its red blood cells.
These causes can be inherited or acquired.” Inherited” means hemolytic anemia occurs
due to shifted gene passed from parents to seeds.” Acquired” means the person isn’t
born with hemolytic anemia, but the condition develops latterly due to failure of his/ her
own vulnerable system. This happens because the vulnerable system inaptly recognizes
these blood cells as foreign. With acquired hemolytic anemias, red blood cells may be
normal. Still, some other complaint or factor causes the body to destroy red blood cells
and remove them from the bloodstream. The destruction of the red blood cells occurs in
the bloodstream or, more generally, in the spleen. Acquired hemolytic anemia can be
divided into
Immune Hemolytic Anemia
and Non-Immune Hemolytic Anemia
TYPES OF ACQUIRED HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA
1. Immune Hemolytic Anemia: In vulnerable hemolytic anemia, the vulnerable system
destroys red blood cells. The three main types of vulnerable hemolytic anemia are
• Autoimmune hemolytic anemia(AIHA)
• Alloimmune hemolytic anemia
• medicine- convinced hemolytic anemia.
I. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia( AIHA):
In this anemia condition, the vulnerable
system makes antibodies( proteins) that attack red blood cells. AIHA accounts
for half of all cases of hemolytic anemia. AIHA may come on veritably snappily
and come serious. Certain conditions or infections can raise the threat for AIHA
are,
• Autoimmune conditions, similar to lupus,
• Habitual lymphocytic leukemia,
• Non-Hodgkin’s carcinoma and other blood cancers,
• Epstein- Barr contagion,
• Cytomegalovirus,
• Mycoplasma pneumonia,
• Hepatitis,
• HIV,
• AIHA also can develop after blood and gist stem cell transplant.
In some types of AIHA, the antibodies made by the body are called warm
antibodies. These are active at warm temperatures and destroy red blood
cells. In other types of AIHA, the body makes cold-reactive antibodies. These
antibodies are active at cold temperatures. Cold-reactive antibodies can
come active when the corridor of the body, similar to the hands or bases, is
exposed to temperatures lower than 32 to 50 ° Fahrenheit( 0 to 10 ° Celsius).
Warm antibody AIHA is more common than cold antibody AIHA.
II. Alloimmune hemolytic anemia: This type of hemolytic anemia occurs if body
makes antibodies against red blood cells that get from a blood transfusion.
This occurs due to a wrong blood transfusion. This type of hemolytic anemia
also can do during gestation if a woman has Rh-negative blood and her baby
has Rh-positive blood.
III. Medicine-convinced hemolytic anemia: Certain drugs alter the normal function of
the vulnerable system, In these cases, the vulnerable system inaptly supposes
the body’s own red blood cells are dangerous, foreign substances. Antibodies
also develop against the red blood cells. The antibodies attach to red blood
cells and beget them to break down too beforehand. Medicines that can beget
this type of hemolytic anemia include Penicillin, Cephalosporin, Dapsone,
Levodopa, Levofloxacin, Methyldopa, Nitrofurantoin, Quinidine,
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines( NSAIDs), and Phenazopyridine.
2. Non-immune hemolytic anemia
Non-Immune Hemolytic Anemia associated with high reticulocyte count, slight or
pronounced increase of lactate dehydrogenase( LDH), increase of indirect bilirubin,
increase of free Hb in the tube with nearly no discovery of haptoglobin and negative
antihuman Immunoglobulin( Coombs) test. Eventually, hemolysis is find
urobilinogen present in urines.
Non-immune hemolytic anemia occurs due to
• Microbial infections like Malaria, babesiosis, septicemia
• Mechanical trauma
• Antiviral agents(e.g., ribavirin)
• Poisons(e.g., snake venom; factory venoms similar as aesculin)
• Paroxysmal nightly hemoglobinuria(rare acquired clonal complaint of red blood cell
face proteins)
• Acute viral hepatitis.
ACQUIRED HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA CAUSES
• Certain chemicals, medicines, and poisons. Infections.
• Transfusion of blood from a patron with a blood type that doesn’t match.
• Certain cancers.
• When antibodies form against red blood cells for no reason, the condition is called
idiopathic autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
• Complication of another type of disease.
• Once blood transfusions.
• Pregnancy( if the baby’s blood type is different from the mama’s).
SYMPTOMS OF ACQUIRED HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA
The symptoms acquired in hemolytic anemia are mild. If the problem develops sluggishly, however, symptoms include
• Feeling weak or tired more frequently than usual, or with exercise.l
• Headaches
• Problems concentrating or thinking
If the anemia gets worse, symptoms may include
• Lightheadedness when you stand up
• Pale skin colour( reddishness)
• Briefness of breath
• Sore tongue
DIAGNOSIS
• Absolute reticulocyte count
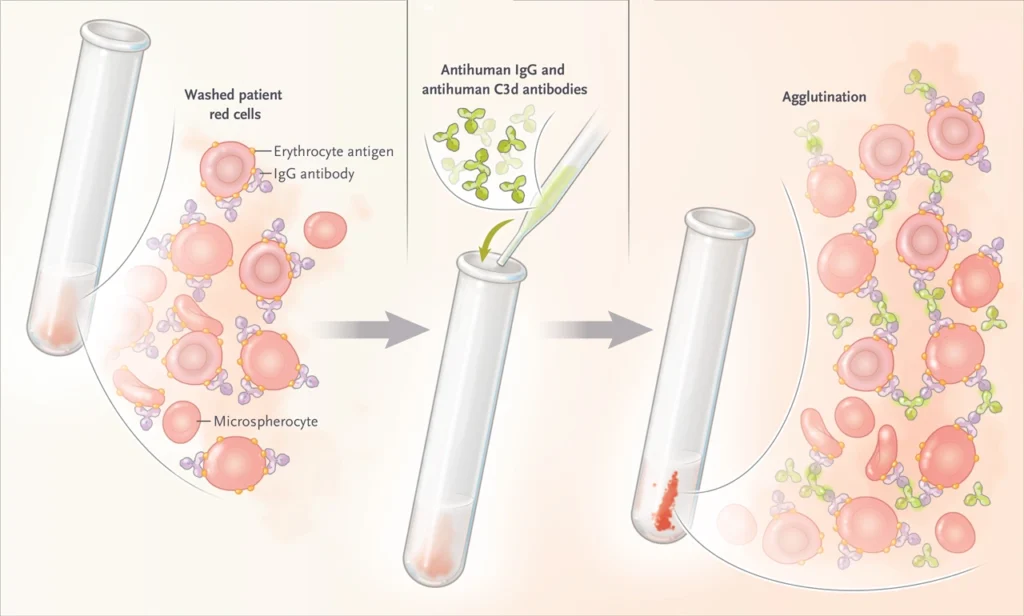
• Direct or circular Coombs test
• Hemoglobin in the urine
• LDH( position of this enzyme rises as a result of towel damage)
• Red blood cell count( RBC), hemoglobin,and hematocrit.
• Serum bilirubin position. Serum free hemoglobin
• Serum haptoglobin
• Donath- Landsteiner test.
• Cold agglutinins
• Free hemoglobin in the serum or urine
• Hemosiderin in the urine
• Platelet count
• Protein electrophoresis-serum.
• Pyruvate kinase.
• Serum haptoglobin position
• Urine and fecal urobilinogen
TREATMENT
The first treatment tried is most frequently a steroid drug, similar to prednisone. However,
treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin( IVIG) or junking of the spleen(
splenectomy) may be considered, If steroid drugs don’t ameliorate the condition. If the
vulnerable system doesn’t respond to steroids. Medicines similar to azathioprine ( Imuran),
cyclophosphamide( Cytoxan), and rituximab( Rituxan) have been used. Blood transfusions
are given with caution because the blood may not be compatible and it may beget
further red blood cell destruction.
PREVENTION
Webbing for antibodies in bestowed blood and in the philanthropist may help hemolytic
anemia related to blood transfusions