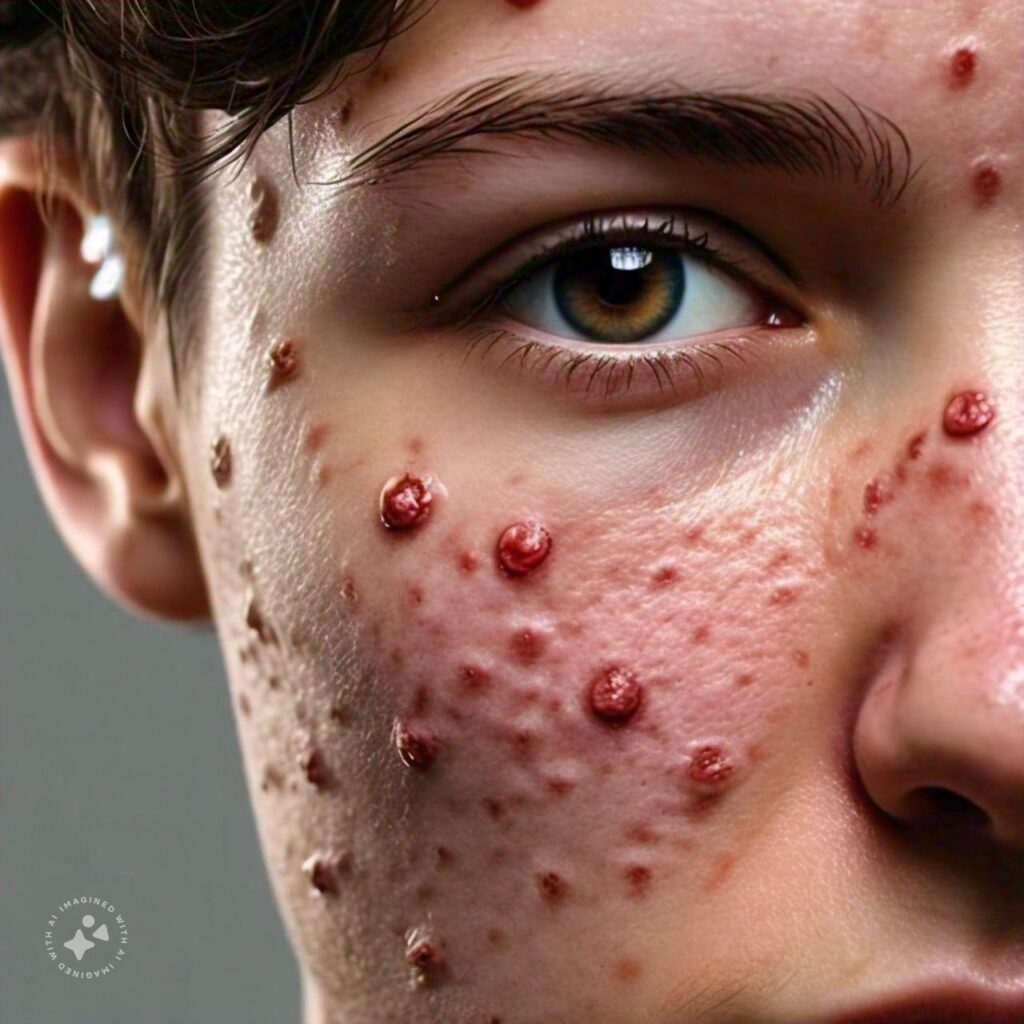
Acne is a skin condition that occurs when the hair follicles become plugged with oil painting and dead skin cells. Acne is a habitual, seditious skin condition that causes spots and pustules, especially on the face, shoulders, back, neck, casket, and upper arms.
TYPES OF ACNE
Acne can take several forms. They include
1) Blackheads: Open bumps on the skin that fill with redundant oil painting and dead skin. They look as if dirt has deposited in the bump, but the dark spots are generally caused due to irregular light reflection off the clogged follicle.
2) Whiteheads: these are the bumps that result in clogged oil and dead skin
3) Papules: Small red or pink bumps that come inflamed.
4) papules pustules containing pus: They look like blackheads girdled by red rings. They can beget scarring if picked or scratched.
5) Fungal acne (pityrosporum folliculitis): This type of acne occurs when the fungus develops in the root of hair follicles. They can come itchy and lit.
6) nodes: they are a collection of tissue. They are hard to the touch and larger than papules, usually 1 to 2 centimetres in diameter. They can vary in colour from flesh-toned to red. Skin tags and warts are examples of nodules.
7) cysts– filled pustules. These can beget scars.
CAUSES OF ACNE
Medical practitioners may believe that one or more of the following can lead to the development of acne:
1) excess oil in the pore.
2) Pore clogged by the dead skin cells
3) Bacterial growth in the pore.
The following are the factors that may make it more likely for an individual to develop acne:
1) Hormones.
3) Medications.
4) Family history
5) Age
The following factors do not cause any type of acne but may make acne worse.
1) Certain foods.
2) Stress.
3) Pressure from sports helmets, tight clothes, or backpacks.
4) Pollution and high humidity.
5) Squeezing or picking at pimples.
6) Scrubbing the skin too hard.
PREVENTION
1) Wash the face no further than doubly each day with warm water and mild cleaner made especially for acne.
2) Don’t drop the skin or burst the pustules, as this may push the infection further down, causing further blocking, swelling, and greenishness.
3) Avoid popping pustules, as this makes scarring likelier.
4) A specialist can treat a papule that requires rapid-fire junking for ornamental reasons.
5) Refrain from touching the face.
6) Hold the telephone down from the face when talking, as it’s likely to contain sebum and skin residue.
7) Wash hands constantly, especially before applying poultices, creams, or makeup.
8) Clean specs regularly as they collect sebum and skin residue.
9) If acne is on the reverse, shoulders, or casket, try wearing loose apparel to let the skin breathe. Avoid tight garments, similar to headbands, caps, and scarves, or wash them regularly if used.
10) Choose makeup for sensitive skin and avoid oil painting- grounded products. Remove makeup before sleeping.
11) Use an electric boychick or sharp safety razors when paring. Soften the skin and beard with warm adulatory water before applying paring cream.
12) Keep hair clean, as it collects sebum and skin residue. Avoid slithery hair products, similar to those containing cocoa adulation.
13) Avoid inordinate sun exposure, as it can cause the skin to produce further sebum. Several acne specifics increase the threat of sunburn.
14) Avoid anxiety and stress, as it can increase the production of cortisol and adrenaline, which complicate acne.
15) Try to keep cool and dry in hot and sticky climates, to help sweating.
TREATMENT OF ACNE
1) Lifestyle: presumably the most useful life change bone can make is to no way to pick or squeeze pustules. Playing with or popping pustules, no matter how careful and clean the bone is, nearly always makes bumps stay redder and bumpier longer. People frequently relate to greenishness as “scarring,” but fortunately, it generally isn’t endless. It’s
just a mark that takes months to fade if left entirely alone.
2) Open the Pores: Occasional visits to an aesthetician who’s an expert at safely removing papules during a facial can be salutary.
3) cleansing and Skin Care: Despite what one might read in popular style and fashion magazines, there’s no magic product or authority that’s right for every person and situation.
i) Mild cleaners: Washing once or doubly a day with a mild sanctification bar or liquid will keep the skin clean and minimize perceptivity and vexation.
ii) slipping cleaners and masks: A variety of mild diminutives, exfoliants, and masks can be used. These products may contain salicylic acid in attention which makes it a veritably mild shelling agent. These products remove the external subcaste of the skin and therefore open pores. Products containing glycolic or nascence hydroxy acids are also gentle
skin exfoliates.
iii) Retinol: Not to be confused with the traditional drug Retin-A- A, this outgrowth of vitamin A can help promote skin shelling.
4) Reducing Bacteria
i) Antibacterial Cleaners: The most popular component of over-the-counter antibacterial cleaners is benzoyl peroxide.
ii) Topical (External) operations: Antibacterial cleaners come in the form of gels, creams, and poultices that are applied to the affected area. The active constituents that kill face bacteria include benzoyl peroxide, sulphur, and resorcinol.
5) Reduce redundant oil
i) One cannot stop oil painting glands from producing oil painting. Indeed, isotretinoin only slows down oil painting glands for a while; they renew normal exertion later.
ii) Use a gentle astringent/ colour to wipe down oil painting.
iii) Products containing glycolic acid or one of the other nascence hydroxy acids are also helpful in clearing the skin by causing the superficial subcaste of the skin to peel(slip).
iv) Masks containing sulphur and other constituents draw out facial oil painting.
v) Antibacterial pads containing benzoyl peroxide have the fresh benefit of helping to wipe down oil secretion.
Buy Best Acne Treatment Products. Below The Link