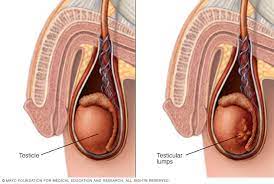
Testicular cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the testicles, which are the male reproductive glands responsible for producing sperm and the male hormone testosterone. It is a relatively rare form of cancer, but it can affect young men and early detection is important. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments of testicular cancer.
Causes of Testicular Cancer:
The exact cause of testicular cancer is not known, but certain factors may increase a man’s risk of developing the disease. Some possible risk factors include:
- Age: Testicular cancer is most commonly diagnosed in young men between the ages of 15 and 35.
- Family history: Men with a family history of testicular cancer are at higher risk of developing the disease.
- Congenital abnormalities: Certain conditions that affect the testicles, such as undescended testicles, may increase the risk of testicular cancer.
- Previous testicular cancer: Men who have had testicular cancer in one testicle are at increased risk of developing it in the other testicle.
- HIV infection: Men with HIV are at increased risk of developing testicular cancer.
Symptoms of Testicular Cancer:
The most common symptom of testicular cancer is a painless lump or swelling in one of the testicles. Other symptoms may include:
- A feeling of heaviness or discomfort in the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort in the testicle or scrotum
- Enlargement of the testicle
- A change in the texture or firmness of the testicle
- A dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin
- Back pain
It’s important to note that not all lumps in the testicles are cancerous, but any changes in the testicles should be evaluated by a doctor.
Treatment of Testicular Cancer:
The treatment of testicular cancer depends on the stage of the disease and other factors such as age and overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: The most common treatment for testicular cancer is surgical removal of the affected testicle, a procedure called a radical orchiectomy. In some cases, lymph nodes in the abdomen may also be removed.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It may be used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It may be used before or after surgery, or as the primary treatment for advanced testicular cancer.
- Surveillance: For some early-stage testicular cancers, a period of surveillance may be recommended to monitor for any changes. This may include regular imaging tests and blood tests.
It’s important for men to be aware of the signs and symptoms of testicular cancer and to perform regular self-examinations of the testicles. Self-examination involves feeling the testicles for any lumps or changes in texture or size. Any changes should be evaluated by a doctor.
In addition to self-examination, men should also have regular physical exams by a healthcare provider. During these exams, the healthcare provider will examine the testicles for any abnormalities and may also order imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI if there are any concerns.
Conclusion:
Testicular cancer is a rare form of cancer that can affect young men. Early detection and treatment are important for the best possible outcome. Men should be aware of the signs and symptoms of testicular cancer, perform regular self-examinations of the testicles, and have regular physical exams by a healthcare provider. If any changes are detected, they should be evaluated by a doctor as soon as possible. Treatment options for testicular cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or surveillance. With proper treatment, the prognosis for most