GOUT:
Gout is a metabolic disorder which is characterized by elevated uric acid levels in blood (serum) and that is deposits of urate crystals in synovial fluids and surrounding tissues in joints. It is a type of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of joint pain with redness, warmth, and swelling in the affected area. The gout usually attacks only one joint at a time. It most often strikes the joint of the big toe, where it is also known as podagra, but other toes can also be involved.Gout affects about 1-2% of the Western population at some point in their lifetimes, and is becoming more common nowadays. Gout rates have about doubled between 1990 and 2010.
This rise is believed due to increasing life expectancy, changes in their diet, and also an increase in diseases associated with gout, such as metabolic disorders and high blood pressure. A many number of factors have been found to influence rates of gout, including age, race, and also the season of the year. In men over the age of 30 and women over the age of 50, prevalence is 2%.Some studies have found that attacks of gout occur more frequently in the spring. This has been attributed to seasonal changes in diet, alcohol consumption, physical activity and also the temperature.
CAUSES OF GOUT:
Gout is caused initially by an excess of uric acid in the blood called as hyperuricemia. Uric acid is produced in the body through the catabolism of purines specific chemical compounds that are found in certain foods like meat, poultry and seafood. Usually, uric acid dissolves in the blood and is excreted from the body in form of urine that is through the kidneys. If too much uric acid is produced in the body or uric acid is not enough is excreted then it can build up and form the needle-like crystals and gets deposited on joints that cause inflammation and pain in the joints and its surrounding tissue.
There are many numbers of factors that can increase the likelihood of
hyperuricemia(excess uric acid) and therefore gout:
• Age and gender: Men produce more uric acid when compared to women. But after menopause, the uric acid level in women increases and become equal to men.
• Genetics: A family history of gout increases the likelihood of the condition
developing gout
• Lifestyle Factors: more Alcohol intake interferes with the removal of uric acid from the body. Eating a high-purine diet also cause increases in amount of uric acid in the body.
• Lead exposure: Chronic lead exposure has been linked in some cases to cause gout.
• Medications: Certain medications are also able to increase the levels of uric acid in the body, including diuretics and drugs containing salicylate, Niacin etc.
• Weight: Being overweight also increases the risk of gout as there is more tissue in the body for turnover or breakdown, leading to the production of excess uric acid in blood.
• Other health problems: If the kidneys are unable to eliminate or excrete waste
products adequately (renal insufficiency) then uric acid levels can remain high in
body. Other conditions that can contribute gout include high blood pressure
(hypertension), diabetes and hypothyroidism. Patients with Kelley-Seegmiller syndrome or Lesch-Nyhan syndrome have a partial or complete deficiency in an enzyme that helps to control uric acid levels.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS:
The signs and the symptoms of gout are almost always acute, which occur suddenly often at night and without warning.
• Intense joint pain: Gout usually affects the large joint of big toe, but it can occur in feet, ankles, knees, hands and wrists. The pain is more severe within the first 12 to 24 hours after it begins.
• Lingering discomfort: After the most severe pain subsides, some joint discomfort
may last from a few days to a few weeks. Later attacks are likely to last longer and affect more joints.
• Inflammation and redness: The affected joint or joints become swollen, tender and red.
GOUT SYMPTOMS:
• Severe pain in joints
• Bone erosion
• Redness
• Swelling in joints
• Mild fever
• Big toe
• Joint stiffness
FOODS THAT CAUSE GOUT:
High purine rich foods are responsible for causing gout including,
• Seafood’s like mussels, tuna, herring, shellfish, shrimp, anchovies
• Red meat(liver)
• Soft drinks
• Alcohol
• Game meat
BEST FOODS FOR GOUT:
• Cherries and vitamin C fruits
• Coffee
• Milk
• Water
• Vegetables
• Whole grain bread
• Brown rice
• Nuts and seeds
COMPLICATIONS OF GOUT:
People who suffering with gout can able to develop more- severe conditions, such as:
• Recurrent gout: Some people may never experience the signs and symptoms of the gout again. But other people may experience gout several times in every year.
Medications will helps to prevent the attack of gout in people with recurrent gout.
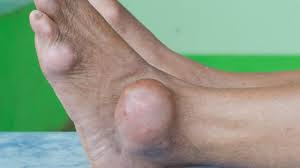
• Advanced gout: If gout is left untreated then it may cause deposits of urate crystals to form under the skin in nodules called as tophi. Tophi can develop in several areas such as fingers, hands, feet, elbows or achilles tendons along the back of ankle. Tophi usually are not painful, but they can cause inflammation and tender during gout attacks.
• Kidney stones: Urate crystals will deposit on the urinary tract of people who
suffering from gout and causes formation of kidney stones.
• Severe degenerative arthritis
• Increase in susceptibility to infections
• Decreased kidney function
• Kidney failure
• Emotional and psychological problems
• Heart disease
• Diabetes
• Sleeping problems
PREVENTION:
During symptom free periods, the following dietary guidelines will helps to protect
against future gout attacks.
• Drink 8 to 16 cups (about 2 to 4 litres) of fluid each day, with at least half being
water.
• Eat a moderate amount of protein, preferably from healthy sources, such as low-fat or fat-free dairy, eggs, and nut butters.
• Limit daily intake of purine rich foods like meat, fish and poultry to 4 to 6 ounces
(113 to 170 grams). Maintain a desirable body weight.
DIAGNOSIS OF GOUT:
1. Joint fluid test: Joint fluid test (arthrocentesis) is useful to detect whether uric acid crystals are present in the joint. This is the only test for diagnosis of gout.
2. Blood test: this test will measure the level of uric acid present in blood. Blood test results can be misleading, though some people have high uric acid levels in blood, but they never experience gout. And some people have signs and symptoms of gout, but they do not have unusual levels of uric acid in the blood.
3. Urine Test: This test will measure the uric acid levels in urine.
4. X-ray: X-rays of extremities (hands and feet) are sometimes useful in the late stages of the disease; X-rays are not usually helpful in the early diagnosis. Severe pain often causes people to seek medical attention before any long-term changes can be seen on an X-ray. But X-rays will help to find out other causes of arthritis.
GOUT TREATMENT:
The main goals of treatment for gout include fast pain relief and prevention of future gout attacks and to prevent long-term complications, like joint destruction and kidney damage.
• NSAIDs: NSAIDS will control inflammation and pain in people with gout. NSAIDs
include indomethacin, ibuprofen, naproxen, and etoricoxib.
• Colchicine: A type of pain reliever (analgesic)that effectively reduces gout pain,
especially when started soon after symptoms appear.
• Corticosteroids: Corticosteroid are those that may control the inflammation of join and reduce the pain. Medications, such as the drug prednisone. Corticosteroids may be administered in pill form, or they can be directly injected into joints. Corticosteroids are generally prefer for those people who cannot take either NSAIDs or colchicine medications.
• Medications that block uric acid production: Xanthine oxidase inhibitors, including allopurinol and febuxostat, limit the amount of uric acid that the body makes. This may lower blood’s uric acid level and reduce risk of gout. Side effects of taking allopurinol include a rash and may leads to low blood counts. Febuxostat drug side effects include rash, nausea and vomiting and also cause reduced liver function. If gout symptoms have occurred OFF and ON without treatment for more than 10 years, uric acid crystals may deposit in the joints to form gritty, chalky nodules called as tophi. If tophi are responsible for causing infection, pain, pressure, and deformed joints, then treatment of gout includes: Xanthine oxidase inhibitors, which may shrink the tophi until they disappear.
• Medication that improves uric acid removal: drug Probenecid will improves
kidney’s ability to remove excess uric acid from the body. This leads to lower uric
acid levels in blood and reduce the risk of gout, but the level of uric acid in urine is
increased.
• Pegloticase: This medicine is used only for the treatment of gout that has lasted a long time and will not responded to other treatments.