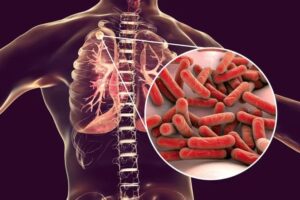
Tuberculosis is also called TB. Tuberculosis is a chronic bacterial infectious disease caused by various strains of Mycobacterium, especially Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis is characterized pathologically by the formation of granulomas. It is transmitted through respiratory water droplets. The main organ affected by tuberculosis is the lungs, but can even spread through the bloodstream and lymphatic system to the brain, GIT system, bones, eyes, joints, and even the skin. In developing countries, it is a major public health problem. India has the highest number of TB cases in the world. Tuberculosis is also an enormous socioeconomic burden to India with one-fifth of the global TB burden borne by India alone, accounting for approximately 1000 death every day. Though the disease’s burden in terms of incidence, it is yet a major public health problem.
There are mainly three stages of TB include primary infection, latent
TB and active TB.
TUBERCULOSIS IS CAUSED BY?
TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Other strains of which are
responsible for causing tuberculosis include,
• Mycobacterium Avium
• Mycobacterium Bovis
• Mycobacterium Hominis
• Mycobacterium Microtia
• Mycobacterium Canetti
• Mycobacterium Africanum
• Mycobacterium Pinnipedii
SYMPTOMS OF TUBERCULOSIS:
• Persistent cough
• Coughing up blood
• Weight
• Fatigue
• Fever
• Night sweats
• Chills
• Loss of appetite(anorexia)
• Urine discoloration
• Low-grade fever
• Chest pain
• Chest tightness
• Cough with sputum
• Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
MODE OF TRANSMISSION:
• It is transmitted through the respiratory route. The organism may present in
water droplets and expel during coughing, sneezing, or talking. Either in
droplets from or as the desiccated air-borne bacilli, the organism enters the
respiratory tract.
• Transmitted through saliva by swallowing infected sputum.
• Ingestion of tubercle bacilli from the milk of diseased cow.
• Also transmitted by transplacental (infected mother to fetus).
What is the incubation period?
The incubation period of tubercule bacilli is 2-12 weeks.
RISK FACTORS:
• Close contact with someone who has active TB
• Immunocompromised patients (HIV, cancer, and prolonged use of corticosteroids)
• Any person without adequate health care
• Pre-existing medical conditions like DM, malnutrition
• Who living in overcrowded, substandard housing
• Healthcare workers
COMPLICATIONS OF TB:
Without treatment, TB can lead to death. Complications include
• Heart disorders
• Meningitis
• Joint damage
• Spinal pain
• Stiffness
• Impaired liver or kidney functions
TYPES OF TB:
1. Pulmonary TB
Tubercle bacilli reach the alveoli and are ingested by pulmonary macrophages.
TB affects the lungs/respiratory tract.
• Primary TB: A person is getting exposed to mycobacterium TB for the first time.
This type of TB is usually occurring in children.
• Secondary TB: If a person is developing TB after a long period of time. Second-time infection. This type of TB is also called post-primary TB.
2. Extrapulmonary TB
TB which affects parts of the body other than the respiratory tract include,
• Lymph node TB: lymph node TB causes the swelling of one or more lymph
nodes. TB lymph nodes can appear in the areas like neck and are sometimes rare in
the groin and also present in organs like mesenteric lymph nodes.
Complications: enlargement of lymph nodes, compression of nerves
Symptoms: weight loss, sweats, fever, and asthenia (body weakness)
• Pleural TB: usually involves the pleura and is common in Primary TB this TB is
results from penetration of tubercle bacilli into pleural space.
Symptoms: chest pain, nonproductive cough, dyspnea
• Genitourinary TB: It is developed in the urinary tract or other genital organs due to
the hematogenous spread of chronic pulmonary TB
Symptoms: Urinary frequency, painful urination, and blood in the urine
• Meningitis TB: the M. Tuberculosis bacteria spread to the brain.
Symptoms: loss of appetite, tiredness, persistent cough, and neck stiffness
Risk factors: HIV/AIDS, excess consumption of alcohol, weakened immune
system and patients with pulmonary TB
Complications: Hyponatremia, seizures and epilepsy, visual impairment,
hydrocephalus and stroke
• Skeletal TB: it involves the TB in bones and joints. This type of TB is not get
transmitted by air. It can transmit through the blood when you come in contact
with an infected person’s body fluids or even the pus.
Symptoms: severe back pain, stiffness, soft tissue swelling and
inflammation of joints
• Gastrointestinal TB: Involvement of TB in any part of the gastrointestinal tract
Symptoms: diarrhea, weight loss, and abdominal pain.
• Miliary TB: Miliary TB is a form of hematogenous disseminated TB. It usually
caused by the sudden diffuse dissemination of the tubercle bacilli through the
bloodstream.
Symptoms: weight loss, fever, chills, weakness, breathing difficulties.
bone marrow infection and Anemia
TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION:
• Live a healthy lifestyle
• If u have a latent infection take all medications properly
• Active TB patients, limit contact with other people
• Cover the mouth while laughing, sneezing, or coughing
• Don’t touch your face
• Wear a mask
• Don’t split around
• Immunization
HOME REMEDIES:
1. Oranges: Rich in vitamin C and helps to reduce the congestion of the lungs and
respiratory tract.
2. Brahmi: Relieve stress and is useful in treating respiratory conditions
3. Banana: It can quickly boost energy and speed up the recovery from TB
4. Milk: Rich in calcium and vitamin D. This will help is helping to treat the severe
symptoms of TB
5. Green tea: It is very rich in antioxidants and helps to boost the immunity system
6. Pine apple: This helps to reduce the production of mucus
7. Mint: It has antibacterial properties and which helps in healing the damaged
tissue.
8. Black pepper: It shows an anti-inflammatory property. It is an effective remedy to
clean the lungs and reduce the production of mucus
9. Garlic: Garlic contains a sulphuric acid which helps to fight against bacteria which
is responsible for causing tuberculosis and strengthening the immune system
10. Amla: Shows antibacterial properties, which helps in accelerating the process of
healing by combating bacteria of tuberculosis
11. Honey: It prevents the adverse effects or side effects caused by drugs that are used to treat TB
12. Gourds: Helps in increasing the immunity
13. Indian gooseberry: Will reduce the severe symptoms of TB and stimulate the
immune system
DIAGNOSIS TUBERCULOSIS:
• Blood test: This test measures the immune system’s reaction to a tuberculosis
bacteria(mycobacterium tuberculosis)
• Sputum culture test: Sputum obtained by coughing is collected and examined in the laboratory and then the sputum is tested for TB bacteria
• Tuberculin skin test: This test is also known as the Mantoux test. This test determines whether a person is infected with TB or not by injecting the tuberculin solution into the skin of the lower arm and checking for a reaction
• X-ray: Pulmonary TB can be easily seen on an X-ray. It shows if any changes in
the lungs
TUBERCULOSIS TREATMENT:
• First-line drugs: These drugs have high antitubercular efficacy as well as low
toxicity, these drugs are used routinely including Isoniazid
Rifampin
Pyrazinamide
Ethambutol
Streptomycin
• Second-line drugs: These drugs have either low antitubercular efficacy or high
toxicity or both. These drugs are used in special circumstances only and include
Ethionamide
Cycloserine
Kanamycin
Capreomycin
Amikacin
• Vaccination: Bacille Calmette Guerin(BCG) is primarily used vaccine against the
tuberculosis.
 Essential Tuberculosis Paperback Buy Now
Essential Tuberculosis Paperback Buy Now